What is periodontal disease?
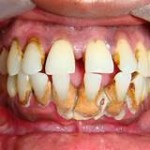
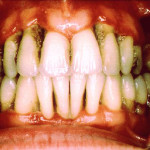
Periodontal diseases are mainly the results of infections and inflammation of the gums and bone that surround and support the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums can become swollen and red, and they may bleed. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or even fall out. Periodontal disease is mostly seen in adults. Periodontal disease and tooth decay are the two biggest threats to dental health.
According to survey more than half of American have some form of gum disease. Gum disease in early stage does not really ring an alarming bell on patients because it presents no pain besides mild inflamation and bleeding when brushing. That is why so many people delay seeking professional care and let it go unchecked.
Causes
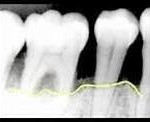
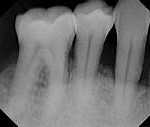
Bacteria in the mouth infect tissue surrounding the tooth, causing inflammation around the tooth leading to periodontal disease. When bacteria stay on the teeth long enough, they form a film called plaque, which eventually hardens to tartar, also called calculus. Tartar build-up can spread below the gum line, which makes the teeth harder to clean. Then, only a dental health professional can remove the tartar and stop the periodontal disease process.
Warning signs
The following are warning signs of periodontal disease:
- Bad breath or bad taste that won’t go away
- Red or swollen gums
- Tender or bleeding gums
- Painful chewing
- Loose teeth
- Sensitive teeth
- Gums that have pulled away from your teeth
- Any change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
- Any change in the fit of partial dentures
Risk factors
Certain factors increase the risk for periodontal disease:
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Poor oral hygiene
- Stress
- Heredity
- Crooked teeth
- Underlying immuno-deficiencies—e.g., AIDS
- Fillings that have become defective
- Taking medications that cause dry mouth
- Bridges that no longer fit properly
- Female hormonal changes, such as with pregnancy or the use of oral contraceptives
Prevention and treatment
Gingivitis can be controlled and treated with good oral hygiene and regular professional cleaning. More severe forms of periodontal disease can also be treated successfully but may require more extensive treatment. Such treatment might include deep cleaning of the tooth root surfaces below the gums, medications prescribed to take by mouth or placed directly under the gums, and sometimes corrective surgery.
To help prevent or control periodontal diseases, it is important to:
- Brush and floss every day to remove the bacteria that cause gum disease.
- See a dentist at least once a year for checkups, or more frequently if you have any of the warning signs or risk factors mentioned above.
Gum Disease and Heart Disease
Several studies have shown that periodontal disease is associated with heart disease. While a cause-and-effect relationship has not yet been proven, research has indicated that periodontal disease increases the risk of heart disease.
Scientists believe that inflammation caused by periodontal disease may be responsible for the association.
Periodontal disease can also exacerbate existing heart conditions. Patients at risk for infective endocarditis may require antibiotics prior to dental procedures. Your periodontist and cardiologist will be able to determine if your heart condition requires use of antibiotics prior to dental procedures.
Stroke
Additional studies have pointed to a relationship between periodontal disease and stroke. In one study that looked at the causal relationship of oral infection as a risk factor for stroke, people diagnosed with acute cerebrovascular ischemia were found more likely to have an oral infection when compared to those in the control group.